contingut
Fecal elastase in stool: what is it?
Fecal elastase is an enzyme produced by the pancreas that plays a role in digestion. Its dosage makes it possible to evaluate the proper functioning of the function of the pancreas associated with digestion.
What is fecal elastase?
The pancreas is an organ of the human body that has two functions:
- an endocrine function for 10% of cells: the pancreas secretes insulin and glucagon, two hormones in charge of regulating the level of sugar in the blood. Insulin lowers blood sugar while glucagon increases it. These two hormones help keep blood sugar levels balanced. If there is a problem with insulin secretion, we talk about diabetes;
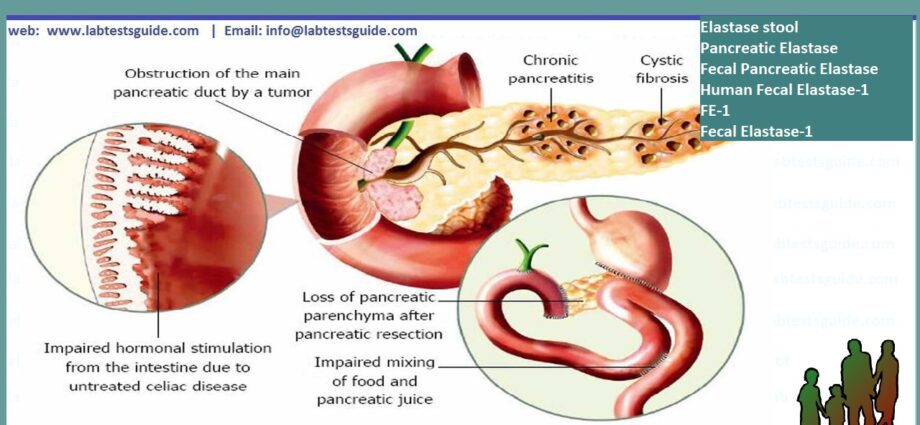
- an exocrine function for 90% of cells: by acinar cells, the pancreas secretes pancreatic enzymes, proteins with a specific role. These enzymes are part of pancreatic juices and are essential for the proper digestion of food. Through the bias of the Wirsung and Santorini channels, the pancreatic juices leave the pancreas to come and mix with the bile in the intestine. In the digestive tract, these enzymes participate in the digestion of fats, proteins and carbohydrates by breaking them down into many elements, more easily assimilated by the body.
Fecal elastase is one of the enzymes produced by the pancreas. It is produced in a stable and constant manner, which makes it a good pancreatic indicator. The purpose of the fecal elastase assay is to assess the proper functioning of the exocrine function of the pancreas. The reference value is 200 micrograms per gram of stool in both adults and children (from one month old). This value is stable and varies little from one day to another in the same person except in the case of severe diarrhea which dilutes the level of fecal elastase. In this case, the analysis will have to be repeated. It is a relatively easy test to perform, which allows it to be substituted for other more difficult tests such as the study of steatorrhea.
Why do a fecal elastase test?
This assay is performed to assess the functioning of the exocrine function of the pancreas. It can for example be carried out in the event of suspicion of exocrine pancreatic insufficiency. It may also be requested by the doctor to determine the causes of a chronic diarrhea problem.
How is a fecal elastase assay performed?
The determination of faecal elastase is carried out on a stool sample. The patient can collect the sample at his home with the material provided by the medical analysis laboratory. He will then quickly drop off the sample in the laboratory for analysis. The sample should be stored at 4 ° C (in the refrigerator). The analysis should be performed within 48 hours of stool collection. This is a sandwich-type ELISA test, specific for human elastase (elastase E1). This test consists of isolating the protein between two antibodies, each recognizing a piece of the protein, thus making it possible to identify and count it.
If the patient is supplemented with enzyme replacement therapy, this has no impact on the dosage of fecal elastase. Conversely, certain things should be avoided the week before and on the day of the sample:
- digestive radiological examinations;
- preparations for colonoscopy;
- laxants;
- intestinal dressings or anti-diarrhea drugs. Indeed, these elements can modify the intestinal flora or falsify the results of the analysis.
Likewise, it is advisable to avoid, if possible, this examination during severe diarrhea. If this is not possible, it should be pointed out so that the doctor can take it into account when analyzing the results.
How to interpret the results of the assay?
A too low level of fecal elastase (except in the case of diarrhea) indicates an insufficiency in the exocrine function of the pancreas. A concentration between 150 and 200 µg / g is an indicator of moderate exocrine pancreatic insufficiency. We speak of major exocrine pancreatic insufficiency when the level of fecal elastase is less than 15 µg / g.
From there, the doctor will need to perform further examinations, tests and imaging to determine the cause of this insufficiency. There are many possibilities:
- pancreatitis crònica;
- pancreatitis aguda;
- fibrosi quística;
- diabetis;
- celiac disease ;
- Crohn’s disease ;
- síndrome de Zollinger-Ellison;
- upper digestive tract surgery;
- etcètera...